If you were to slice a rotary servo motor and lay it flat, you would have, essentially, a linear motor. The rotor with permanent magnets becomes the stationary part of the linear motor (also called the secondary, or magnet plate), and the stator, which contains the coil windings, becomes the moving part (also called the primary, or coil unit).
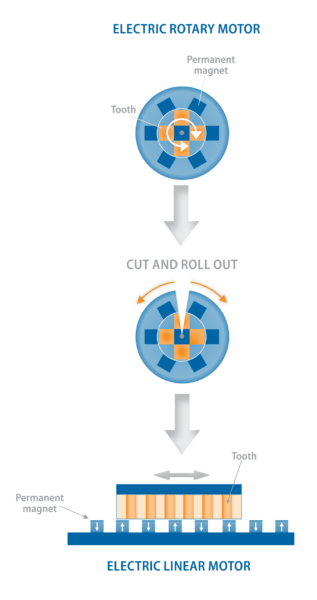
Round motor to electric linear motor
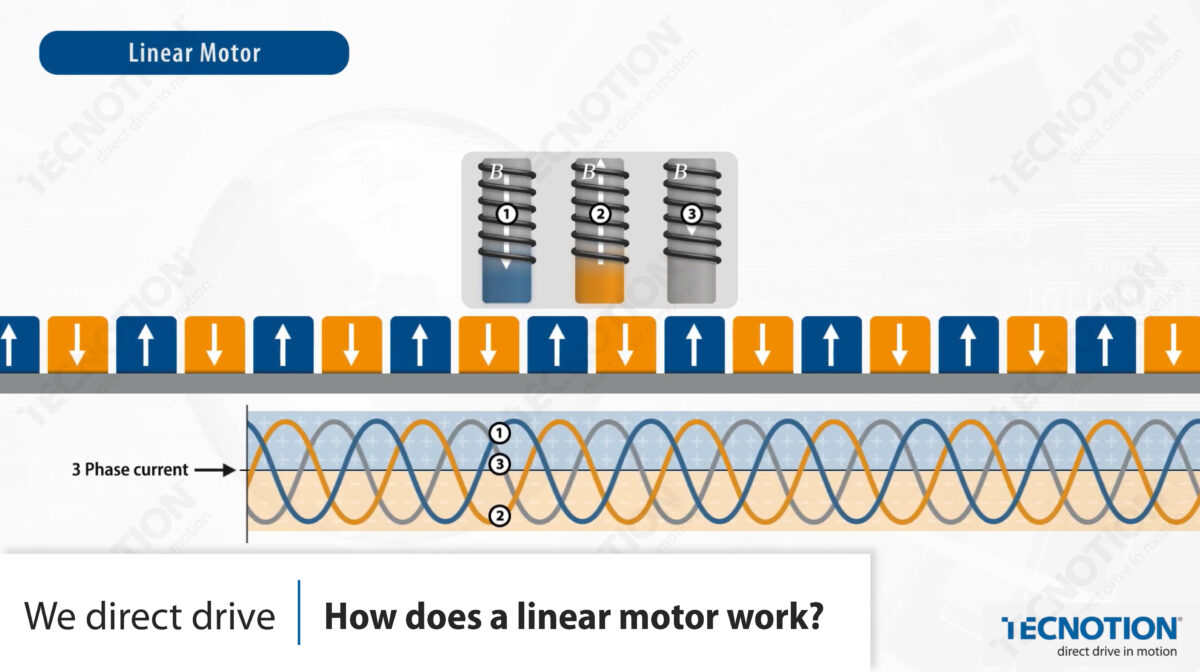
Linear motors operate with an AC power supply and servo controller, which are often the same as those used for rotary servo motors. The linear motor primary part is connected to the power supply to produce a magnet field. By changing the current phase in the coils, the polarity of each coil is changed. The attractive and repelling forces between the coils in the primary part and the magnets in the secondary part cause the primary to move and generate a linear force. The rate of change of the current controls the velocity of the movement, and the amperage of the current determines the force generated.
For more info and specifications, please check our Ironless and Iron core product pages.
Ask us directly

Mike Rolink and Stefan Jansen
Application Engineers
“Do you have a question about a motor? Or do you need technical support during an installation? Call us and one of our Application Engineers will help and support you throughout the entire process.”
Ask your question