What is a Steel Laser Cutting Machine and How Does It Work?
The steel laser cutting machine represents a significant advancement in manufacturing technology. In 2021, the global laser cutting machine market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion, with a projected growth rate of 7.5% annually. This data highlights the increasing demand for precision cutting in various industries.
Steel laser cutting machines utilize high-powered lasers to cut through metal sheets with accuracy. Their ability to create intricate designs makes them indispensable in sectors such as automotive and aerospace. Yet, some manufacturers struggle with high operational costs and maintenance challenges. These hurdles can hinder efficiency and profitability.
Despite these issues, the advantages of steel laser cutting machines are clear. They offer reduced waste and faster production times compared to traditional methods. However, the transition to laser cutting technology may not always be seamless. Companies must carefully consider their specific needs and capabilities before investing heavily in this technology.
What is a Steel Laser Cutting Machine?
A steel laser cutting machine utilizes high-powered lasers to cut through metal. Unlike traditional cutting methods, it offers precision and speed. The process begins with a focused beam of light. This laser beam melts, burns, or vaporizes the metal. As a result, the machine can produce intricate designs with minimal waste.
According to industry reports, the global market for laser cutting machines is expected to reach $5.9 billion by 2027, driven by their efficiency in production. These machines are particularly effective for thick materials. However, maintenance is crucial. Operators must regularly check for alignment and focus to ensure optimal performance. Neglecting these tasks can lead to decreased cutting quality.
The technology is not without challenges. For instance, initial setup costs can be high. Many companies struggle with integrating new machines into existing workflows. Additionally, training staff to operate this complex machinery requires time and resources. Despite these hurdles, the advantages are undeniable. Precision and speed make steel laser cutting machines a valuable asset in manufacturing.
Steel Laser Cutting Machine Efficiency Comparison
Types of Laser Cutting Technologies Used in Steel Cutting
Laser cutting technology has transformed the way steel is processed. There are several types of laser cutting techniques specifically suited for steel cutting. The most prominent are CO2, fiber, and disk lasers. Each type has its unique attributes and advantages.
CO2 lasers are widely used in steel cutting. They produce a high-power beam that effectively cuts through thick sheets. These lasers can be less effective on thin materials. Fiber lasers, on the other hand, excel in cutting thin and medium thicknesses. They are known for their speed and efficiency. Many industries prefer fiber lasers due to their lower operating costs and energy efficiency. Disk lasers combine both qualities. They offer high precision with fast cutting speeds, making them a versatile choice for various applications.
It's crucial to understand that choosing the right laser technology involves trade-offs. Each type presents its own set of challenges. For instance, while fiber lasers are effective, they may require additional considerations for maintenance. The CO2 laser’s ability to cut thick steel is impressive, yet it can lead to slower cutting speeds. Reflecting on these factors is essential for making informed decisions in laser cutting operations.
Components and Mechanism of a Laser Cutting Machine
A steel laser cutting machine comprises several key components that work together to create precise cuts. The core element is the laser generator, which produces a concentrated beam of light. This beam travels through a series of mirrors and lenses. They focus the light onto the material, in this case, steel.
Another important component is the cutting head. It regulates the gas flow, usually oxygen or nitrogen, that assists in the cutting process. The cutting head moves across the steel surface. This movement allows for intricate designs and shapes. A computer control system dictates the path of the cutting head. However, programming errors can lead to uneven cuts, reminding operators to double-check settings.
Cooling systems also play a critical role. They prevent overheating, which can warp the material and affect precision. Regular maintenance is essential, as some parts can wear out quickly. Not all machines achieve uniform performance; older models might struggle with thicker steel. Operators may need to adapt techniques according to the condition of the equipment.
How Steel Laser Cutting Machines Operate in Industrial Settings
Steel laser cutting machines play a crucial role in modern industrial settings. These devices use high-powered lasers to slice through steel with precision. The process begins with focusing the laser beam onto the steel surface. The intense heat melts or vaporizes the material, creating a clean cut. In an industrial environment, operators must monitor the process closely. Any disruption can lead to errors in cutting.
Operators often adjust settings like speed and power based on the steel thickness. A deeper cut requires more energy, while thinner sheets need less. This adjustment process takes skill and practice. Mistakes can lead to wasted materials or incomplete cuts. Therefore, training is essential for effective operation. Even experienced users may face challenges as new materials or designs are introduced.
The machine's software helps in designing cuts, but it is not foolproof. Small errors in design can escalate into significant issues during production. Understanding the limitations of the technology is vital. A keen eye for detail helps in troubleshooting. Regular maintenance of the machine is also necessary. Neglect can lead to subpar performance and compromised quality.
What is a Steel Laser Cutting Machine and How Does It Work?
| Feature |
Description |
| Laser Type |
Fiber Laser |
| Material Thickness |
Up to 25mm for Mild Steel |
| Cutting Speed |
Up to 30 m/min depending on material and thickness |
| Power Consumption |
Typically ranges from 1kW to 10kW |
| Applications |
Used in automotive, aerospace, construction, and metal fabrication |
| Software Compatibility |
Compatible with CAD/CAM software for precise cutting designs |
| Maintenance Frequency |
Regular maintenance every 6 months recommended |
| Operator Skill Level |
Requires trained personnel for operation and troubleshooting |
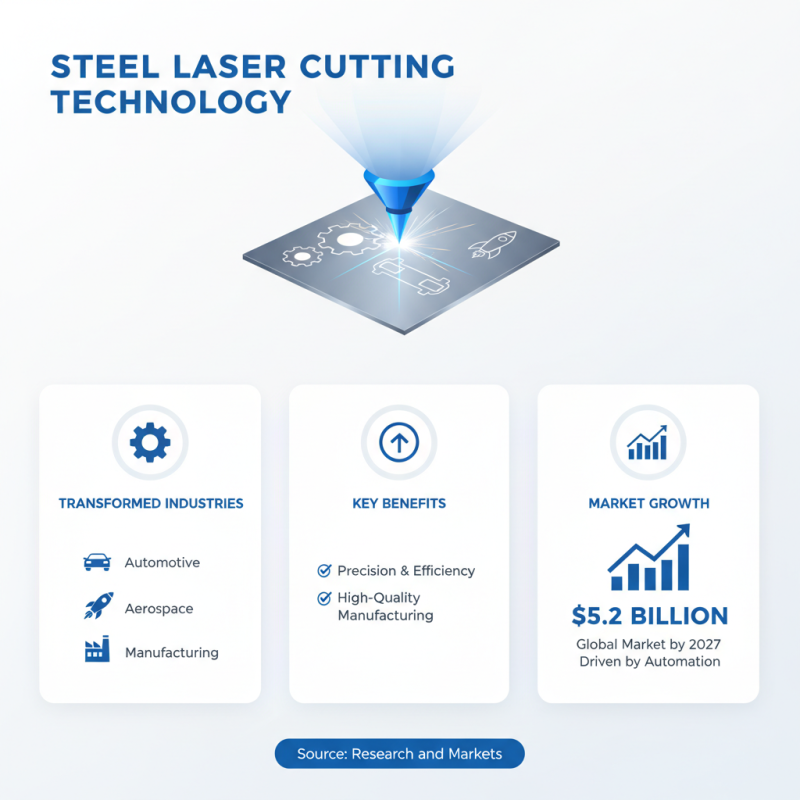
Applications and Benefits of Steel Laser Cutting Technology
Steel laser cutting technology has transformed various industries by providing precise and efficient cutting solutions. This method is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global laser cutting market is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2027, driven by increasing demand for automation and high-quality manufacturing processes.
One significant benefit of laser cutting is its accuracy. It can achieve cuts with a tolerance of ±0.005 inches. This precision minimizes material waste, which is crucial in reducing production costs. Companies have noted an average reduction of 30% in scrap materials when switching to laser cutting. Additionally, the technology allows for complex shapes and designs that traditional cutting methods struggle to produce. However, the initial investment in laser cutting machines can be high, requiring careful financial consideration.
Another aspect to reflect on is the energy consumption associated with laser cutting. Although it’s efficient, the machines may draw significant power during operation. Addressing this energy usage is essential for sustainable practices in manufacturing. The industry must balance the benefits of speed and efficiency against environmental impact. As companies adopt steel laser cutting, ongoing adjustments will be necessary to optimize both performance and sustainability.